Normal Alignment
Align the Z axis of your instances
Normal Alignment
The "Normal Alignment" procedural feature will let you define the default +Z axis of your instances. There are multiple direction methods you can choose from, and each of them can be reversed with the help of the reverse arrow button. If this feature is not enabled, Geo-Scatter will use the default alignment axis generated by your distribution method, please consult the distribution page to review the various default alignments.
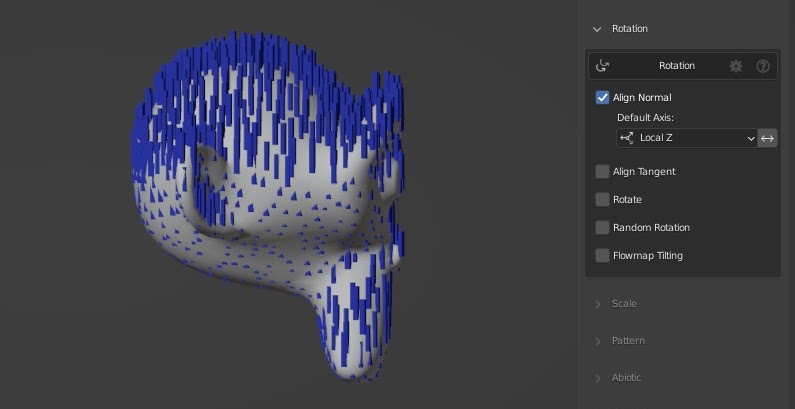
Surface Normal Alignment
Align the normal of your instances with the normal of the faces they are distributed upon. The surface normal will be automatically interpolated to the face set to smooth.
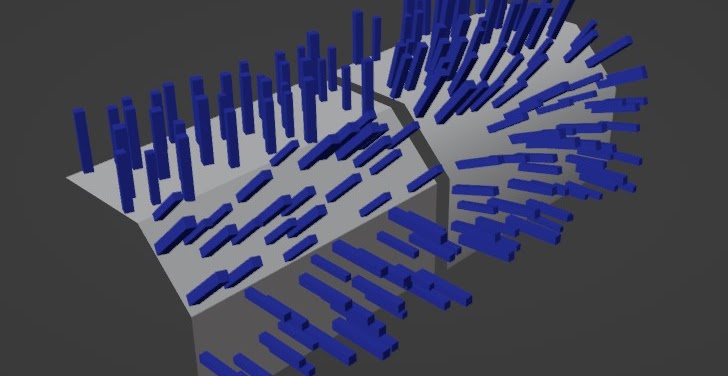
Local/Global Z Alignment
Align the normal of your instances with the Z axis of their local surface space, or with the z-axis of the world space.
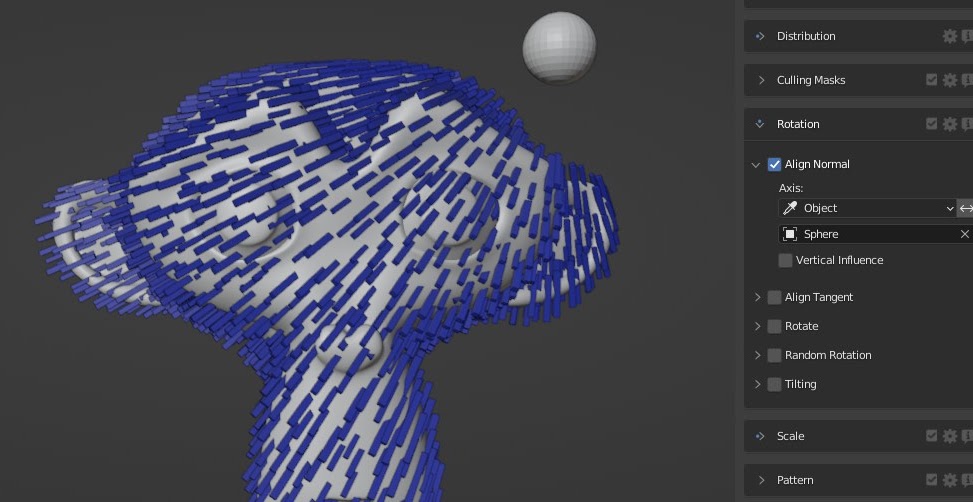
Object Origin Alignment
Align the normal of your instances toward the origin of the chosen object.
If you'd like to only align your normal nearby other objects, please look
at our proximity repel feature.
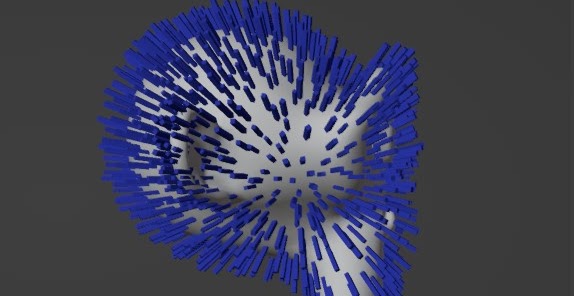
Surface Origin Alignment
Align the normal of your instances toward the origin of their emitting surface.
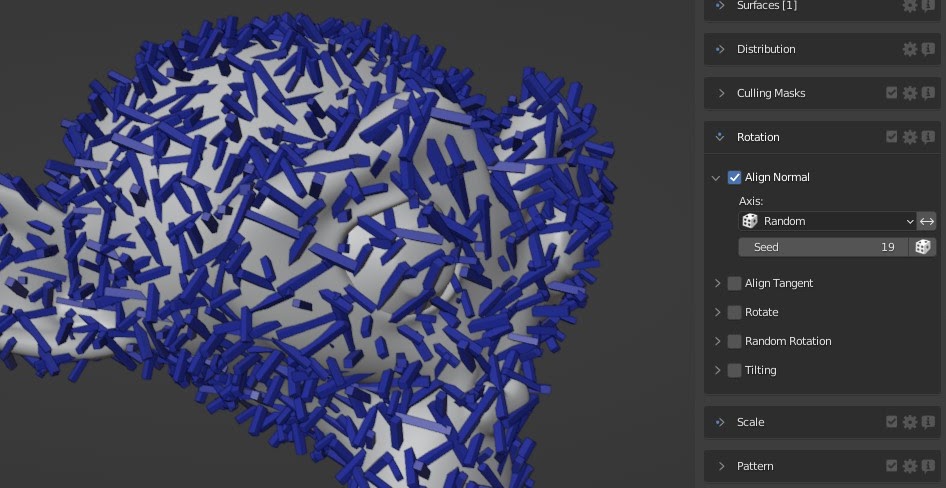
Random Alignment
Choose a random normal axis.
If you'd like more control over the randomization, please look at the
random rotate feature.
Camera Alignment
Align your instances normal toward the active camera. Useful for billboard instances that always need to be tangent toward the active camera.
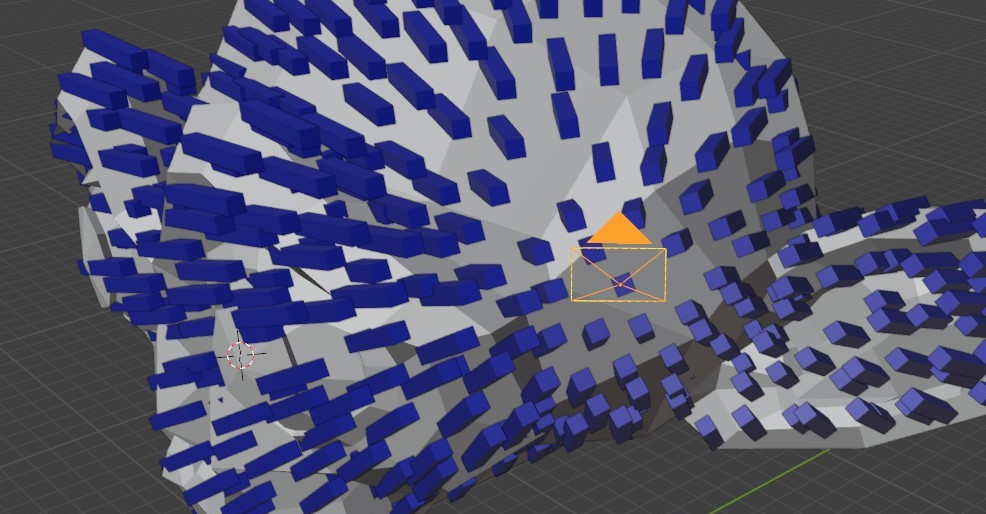
Local vs Global
Here above, is a demonstration of an alignment toward the Local object Z axis, compared to the world Global Z axis.
Smoothing Option
When working with most features that will take the normal of your surfaces into consideration, you will have access to a 'Smoothing' toggle. This option is very useful when you want your computed direction to be an average the neighboring normals, instead of being the exact normal axis.
Vertical Influence
The "Vertical Influence" option can be enabled in if you'd like to mitigate the strength of the normal influence with the world global Z axis.
Tangent Alignment
Align the Y axis of your instances
Tangent Alignment
The "Tangent Alignment" feature will let you define the default +Y axis of your instances. There are multiple directions to choose from, and each of them can be reversed with the help of the reverse arrow button. If this feature is not enabled, Geo-Scatter will use the default axis generated by your distribution method.
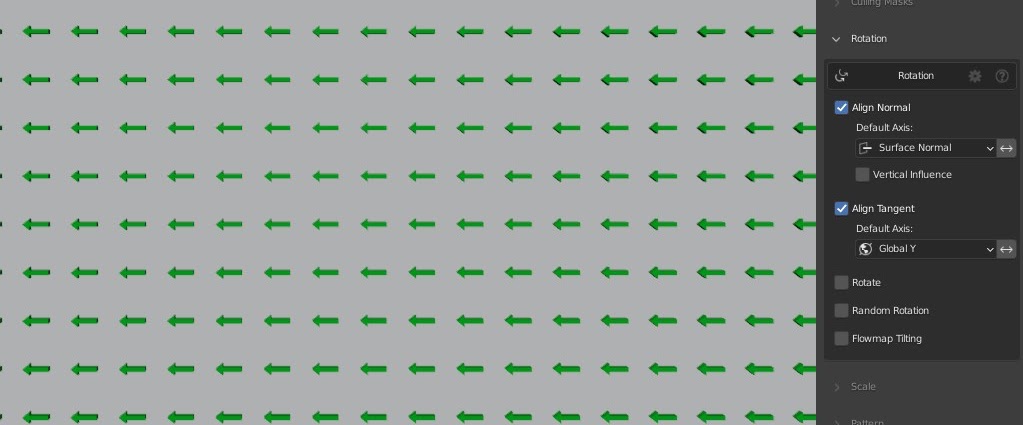

Local/Global Y Alignment
Align the tangent of your instances toward their local surface space Y axis, or use the world space Y axis.
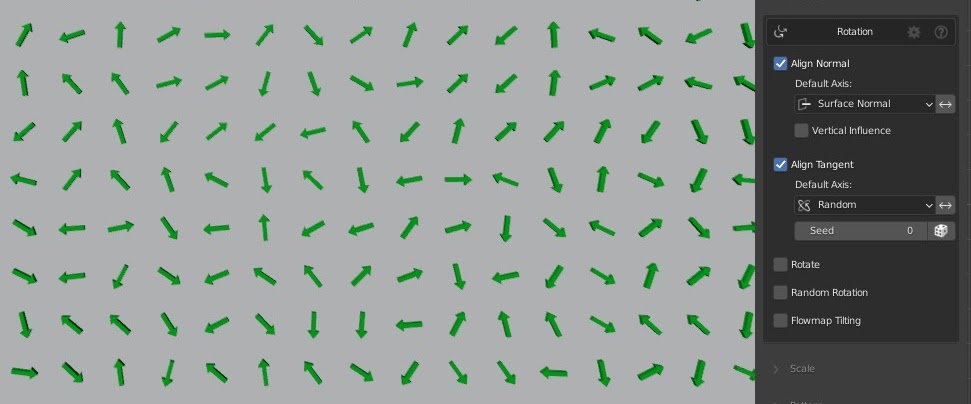
Random Alignment
Align the tangent of your instances toward a random axis.
If you'd like more control over the randomization, please look at the
random rotate feature.
Flowmap Alignment
Control the tangent alignment with the help of a texture or vertex-color flow map data.
Downslope Alignment
Align the tangent of your instances toward the direction of the slope.
Object Origin Alignment
Align the tangent of your instances toward a chosen object origin point.
Camera Alignment
With the camera tangent alignment method, you'll be able to create billboard instances always facing the active camera. (This is how we created the AlphaTrees biome pack).
Edge Boundary Alignment
Align the tangent of your instances toward the closest surface boundary edge loop.
Boundary Hardsurface Demo
The edge boundary tangent alignment method is extremely useful for hardsurface scattering, such as scattering cityscapes, or futuristic greebles.
Pro Tip
Under Display>Display As, there are handy placeholder "helpers" in the form of arrows or colored axis useful to visualize your rotation/alignments more clearly.
Pro Tip
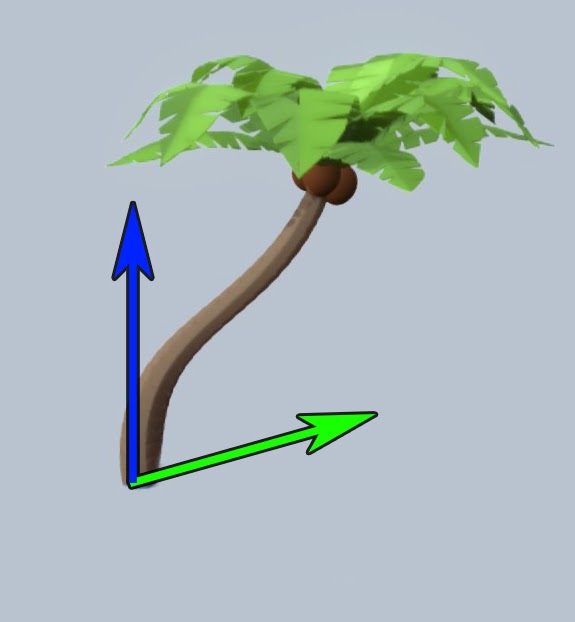
It is always a good idea to orient the original mesh of your instances toward the local +Y direction when you are in edit mode, as +Y is the default 'forward' direction of blender.
Rotate
Rotate your instances
Rotate
The "Rotate" feature adds the defined XYZ Euler angle values/random values to your instance's rotation.
Additionally, there's is a very useful "Snap" slider available, useful to snap your random rotation to 45 or 90 degrees angles, ideal for hard-surface scattering or generating cities landscapes.
Random Rotate
Rotate your instances randomly
Random Rotate
The "Random Rotation" feature will add random tilt/yaw values to your instance's rotation.
If only randomization on Yaw is needed, consider using a random tangent alignment.
Rotation Tilt
Tilt your instances based on a flowmap
Rotation Tilt Feature
If you'd like to create a rotation pattern affecting your scattering, that's where the "Flowmap Tilting" features come in handy. This feature will procedurally tilt your instances depending on a given flowmap, encoded in a scatter texture-data or a vertex-color layer.
Use Case
Replicate tilting patterns of fields, forests, or interior carpets.
Pro Tip
If you'd like to create a wind effect, we advise to use the wind-wave feature instead.
Tilt Flowmap
In the example hereby, we are painting a flowmap encoded within vertex colors. This flowmap will influence your instances tilt, with the help of the Clemens Beute flowmap painter addon
Tilt Strength Influence
You could mitigate the strength of the tilt with a noise feature-mask. It is also possible to use the blue channel of your flowmap to do so.